Chapter 1. ExpressionsWhen a graph is defined by an equation, Advanced Grapher offers the option of different types of operation, consisting of constants and variables and/or their functions, connected by operators.
Operations
- arithmetical operations: +, -, *, /, ^ (raising to power).
Example: 2+2^3=10
Hint: you can use the calculator to check the examples. Click  button to show the calculator (Figure 1.1). button to show the calculator (Figure 1.1). | 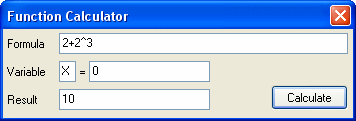
Figure 1.1: Calculator |
- logical operations. The result and operands of these operations may be true or false.
Advanced Grapher doesn't have special values for true and false. If the operand is negative or zero it's false, else it's true. The result of the operations is always 0 (false) or 1 (true). Advanced Grapher supports the following logical operations: AND, OR, XOR and NOT. NOT is an unary operator; AND, OR, XOR are binary operations. You can see results of the operations depending on the value of the operands in the following table:
| Operand 1 | Operand 2 | AND | OR | XOR | NOT | | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | | | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
(The result for the not operation depends on the operand 1 only - not Operand 1).
Examples: 1 or 0=1; 5 and -1=0; (not 3) + 2*(1 xor 0)=2 - relational operations: >,<,>=,<=,=,<>. The result of these operations is 0 (false) or 1 (true). These operations are mostly used to graph systems of inequalities.
Examples: (2>3) = 0; (3<=3) = 1; (0<>1) = 1
Functions
You can use different functions in the expressions. If you'd like to use a function you should enter <name_of_function>(<argument>).
Examples: sin(x+2); ln(ln(1/x)); sin(x)^3. Advanced Grapher allows to use the following functions:
sin - sine
cos - cosine
tan - tangent
cot - cotangent
asin - inverse sine
acos - inverse cosine
atan - inverse tangent
abs - absolute value
sqrt - square root
ln - natural logarithm
lg - logarithm base 10
exp - exponent (exp(x) - e raised to the power x)
int - integer part of number
round - rounded value
frac - fractional part of number
sign - sign(x)=1 if x>0, sign(x)=0 if x=0 and sign(x)=-1 if x<0
sinh - hyperbolic sine
cosh - hyperbolic cosine
tanh - hyperbolic tangent
coth - hyperbolic cotangent
asinh - hyperbolic inverse sine
acosh - hyperbolic inverse cosine
atanh - hyperbolic inverse tangent
acoth - hyperbolic inverse cotangent
random - random(x)=rnd*x, rnd is a random value, 0<=rnd<1
Priority of the operations and functions
1. Functions
2. ^
3. *,/
4. +,-
5. >=,=,<=,<,>,<>
6. not
7. and, or, xor
Functions have the largest priority; and, or, xor - the smallest.
Example: not 1+2 and 0 = (not (1+2)) and 0 = 0
Constants
Advanced Grapher recognizes the constant PI which is directly available. If you wish to use the constant e (base of natural logarithm), type in exp(1).
Variables
You can also use one or two variables, for example X, Y, A or T (it depends on the situation).
Additional information
You can leave out "*". Examples: xy, (x+1)(5y+x), xx, xsin(x).
|